【re:Invent 2024 現地レポート】Amazon Q Developerの新機能紹介

はじめに
新年おめでとうございます、akiraです。 昨年12月に開催されたre:Invent 2024に会社から参加させていただきました。 現地での熱狂や多くの新機能発表にとても刺激を受けました。
今回は新機能の中でも特に気になっているAmazon Q Developerの新機能について紹介したいと思います。
Amazon Q Developerとは
Amazon Q Developerは生成AIを用いた会話アシスタントで、統合開発環境 (IDE) 上でで使用する場合、インラインコード補完や、チャットを用いて新規コードの作成修正の提案などを行ってくれるサービスです。
もともとはAmazon CodeWhispererとして提供されていましたが、Amazon Qに統合され昨年の4月に一般公開されました。

新機能
今回はre:Inventの期間中に発表された機能よりIDE上で利用可能な3機能について紹介します。 その他の発表についてもリンクを掲載しておりますので、ぜひご覧ください。
- サンプルコード
-
class MathOperations: def add(self, a, b): """2つの数値を加算する""" return a + b def subtract(self, a, b): """2つの数値を減算する""" return a - b def multiply(self, a, b): """2つの数値を乗算する""" return a * b def divide(self, a, b): """2つの数値を除算する。ゼロ除算の場合は例外をスローする""" if b == 0: raise ValueError("Division by zero is not allowed.") return a / b def power(self, a, b): """aをb乗した値を返す""" return a ** b
ユニットテスト作成機能
プロンプトから/testを実行するだけで単体テストコードが作成されます。
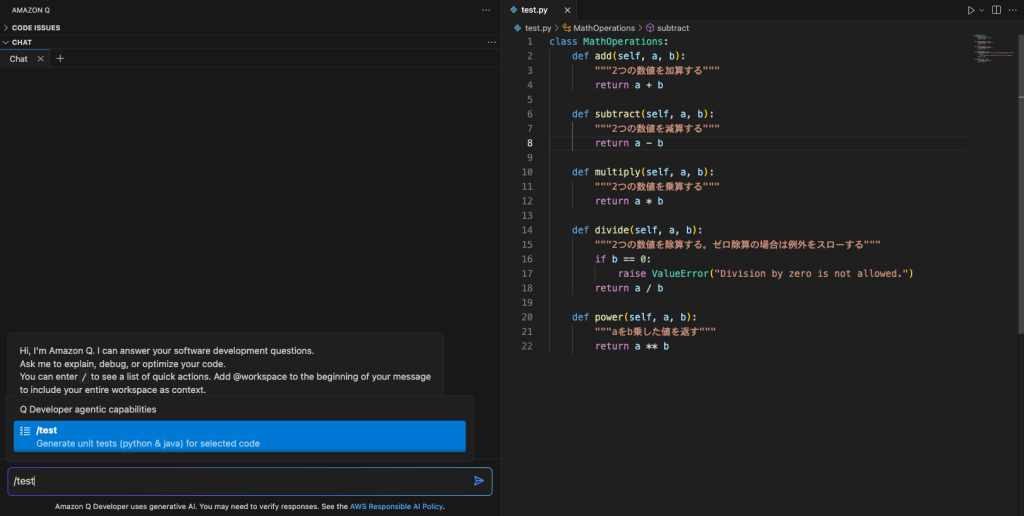
以下の様にテストコードを作成してくれます。
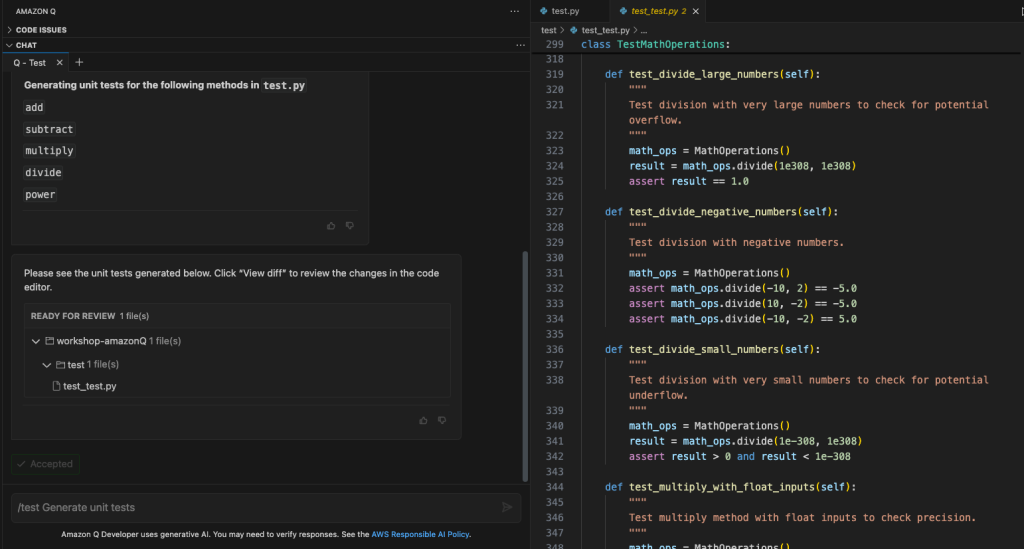
- test_test.py
-
from workshop_amazonQ.test import MathOperations import pytest class TestTest: def test_add_float_overflow(self): """Test add method with float overflow""" math_ops = MathOperations() max_float = float('inf') assert math_ops.add(max_float, 1) == float('inf') assert math_ops.add(1, max_float) == float('inf') assert math_ops.add(max_float, max_float) == float('inf') def test_add_floating_point(self): """ Test adding floating point numbers """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.add(3.14, 2.86) assert pytest.approx(result, 0.001) == 6.0 def test_add_integer_overflow(self): """Test add method with integer overflow""" math_ops = MathOperations() max_int = 2**63 - 1 # Maximum 64-bit signed integer result = math_ops.add(max_int, 1) assert result == 2**63 def test_add_invalid_input_type(self): """Test add method with invalid input types""" math_ops = MathOperations() with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.add("1", 2) with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.add(1, "2") with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.add("a", "b") def test_add_negative_numbers(self): """ Test adding two negative numbers """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.add(-2, -7) assert result == -9 def test_add_negative_zero(self): """Test add method with negative zero""" math_ops = MathOperations() assert math_ops.add(0, -0) == 0 assert math_ops.add(-0, 0) == 0 assert math_ops.add(-0, -0) == 0 def test_add_none_input(self): """Test add method with None input""" math_ops = MathOperations() with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.add(None, 2) with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.add(1, None) with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.add(None, None) def test_add_positive_and_negative(self): """ Test adding a positive and a negative number """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.add(10, -4) assert result == 6 def test_add_positive_numbers(self): """ Test adding two positive numbers """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.add(3, 5) assert result == 8 def test_add_zero(self): """ Test adding zero to a number """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.add(5, 0) assert result == 5 def test_divide_1(self): """ Test that divide method correctly performs division for non-zero divisor. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.divide(10, 2) assert result == 5.0, f"Expected 5.0, but got {result}" def test_divide_2(self): """ Test division with positive and negative numbers. """ math_ops = MathOperations() assert math_ops.divide(15, 3) == 5.0 assert math_ops.divide(-10, 2) == -5.0 assert math_ops.divide(7, -2) == -3.5 assert math_ops.divide(-8, -4) == 2.0 assert math_ops.divide(1, 3) == pytest.approx(0.3333333333333333) def test_divide_non_zero_denominator(self): """ Test division with non-zero denominator. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.divide(10, 2) assert result == 5.0, "Expected 10 / 2 to equal 5.0" def test_divide_raises_value_error_on_zero_division(self): """ Test that divide method raises ValueError when dividing by zero. """ math_ops = MathOperations() with pytest.raises(ValueError, match="Division by zero is not allowed."): math_ops.divide(10, 0) def test_multiply_by_zero(self): """ Test multiplication by zero """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.multiply(5, 0) assert result == 0, "Multiplication of any number by 0 should be 0" def test_multiply_floating_point(self): """ Test multiplication of floating point numbers """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.multiply(2.5, 3.2) assert pytest.approx(result, 0.0001) == 8.0, "Multiplication of 2.5 and 3.2 should be approximately 8.0" def test_multiply_negative_numbers(self): """ Test multiplication of two negative numbers """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.multiply(-2, -5) assert result == 10, "Multiplication of -2 and -5 should be 10" def test_multiply_positive_and_negative(self): """ Test multiplication of a positive and a negative number """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.multiply(3, -4) assert result == -12, "Multiplication of 3 and -4 should be -12" def test_multiply_positive_numbers(self): """ Test multiplication of two positive numbers """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.multiply(3, 4) assert result == 12, "Multiplication of 3 and 4 should be 12" def test_power_1(self): """ Test power method with various inputs including edge cases. """ math_ops = MathOperations() # Test with positive integers assert math_ops.power(2, 3) == 8 # Test with negative base assert math_ops.power(-2, 3) == -8 # Test with zero base assert math_ops.power(0, 5) == 0 # Test with exponent 0 assert math_ops.power(5, 0) == 1 # Test with exponent 1 assert math_ops.power(7, 1) == 7 # Test with fractional exponent assert pytest.approx(math_ops.power(4, 0.5)) == 2 # Test with negative exponent assert pytest.approx(math_ops.power(2, -2)) == 0.25 def test_power_positive_integers(self): """ Test power method with positive integer base and exponent. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.power(2, 3) assert result == 8, f"Expected 2^3 to be 8, but got {result}" def test_power_with_complex_result(self): """ Test power method with inputs that would result in a complex number. """ math_op = MathOperations() with pytest.raises(ValueError): math_op.power(-1, 0.5) def test_power_with_float_exponent(self): """ Test power method with float exponent, which is valid but might be considered an edge case. """ math_op = MathOperations() assert math_op.power(2, 2.5) == 5.656854249492381 def test_power_with_invalid_input_types(self): """ Test power method with invalid input types. """ math_op = MathOperations() with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_op.power("2", 3) with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_op.power(2, "3") with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_op.power(None, 3) with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_op.power(2, None) def test_power_with_large_exponent(self): """ Test power method with a very large exponent to check for potential overflow. """ math_op = MathOperations() with pytest.raises(OverflowError): math_op.power(2, 1000000) def test_power_with_negative_exponent(self): """ Test power method with negative exponent. """ math_op = MathOperations() assert math_op.power(2, -2) == 0.25 def test_power_with_zero_base(self): """ Test power method with zero as the base. """ math_op = MathOperations() assert math_op.power(0, 5) == 0 assert math_op.power(0, 0) == 1 def test_subtract_float_numbers(self): """ Test subtracting float numbers. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.subtract(5.5, 3.3) assert pytest.approx(result, 0.0001) == 2.2 def test_subtract_negative_from_positive(self): """ Test subtracting a negative number from a positive number. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.subtract(5, -3) assert result == 8 def test_subtract_negative_numbers(self): """ Test subtracting two negative numbers. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.subtract(-5, -3) assert result == -2 def test_subtract_positive_from_negative(self): """ Test subtracting a positive number from a negative number. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.subtract(-5, 3) assert result == -8 def test_subtract_positive_numbers(self): """ Test subtracting two positive numbers. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.subtract(5, 3) assert result == 2 def test_subtract_zero(self): """ Test subtracting zero from a number and subtracting a number from zero. """ math_ops = MathOperations() assert math_ops.subtract(5, 0) == 5 assert math_ops.subtract(0, 5) == -5 assert math_ops.subtract(0, 0) == 0 class TestMathOperations: def test_divide_by_zero(self): """ Test that dividing by zero raises a ValueError. """ math_ops = MathOperations() with pytest.raises(ValueError, match="Division by zero is not allowed."): math_ops.divide(10, 0) def test_divide_invalid_type(self): """ Test that dividing with non-numeric types raises a TypeError. """ math_ops = MathOperations() with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.divide("10", 2) with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.divide(10, "2") def test_divide_large_numbers(self): """ Test division with very large numbers to check for potential overflow. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.divide(1e308, 1e308) assert result == 1.0 def test_divide_negative_numbers(self): """ Test division with negative numbers. """ math_ops = MathOperations() assert math_ops.divide(-10, 2) == -5.0 assert math_ops.divide(10, -2) == -5.0 assert math_ops.divide(-10, -2) == 5.0 def test_divide_small_numbers(self): """ Test division with very small numbers to check for potential underflow. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.divide(1e-308, 1e308) assert result > 0 and result < 1e-308 def test_multiply_with_float_inputs(self): """ Test multiply method with float inputs to check precision. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.multiply(0.1, 0.2) assert pytest.approx(result, 0.00001) == 0.02 def test_multiply_with_invalid_types(self): """ Test multiply method with invalid input types. """ math_ops = MathOperations() with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.multiply("2", 3) with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.multiply(2, "3") with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.multiply(None, 3) def test_multiply_with_large_numbers(self): """ Test multiply method with numbers at the edge of integer bounds. """ math_ops = MathOperations() max_int = 2**31 - 1 # Maximum 32-bit integer assert math_ops.multiply(max_int, 2) == max_int * 2 assert math_ops.multiply(-max_int, 2) == -max_int * 2 def test_multiply_with_negative_numbers(self): """ Test multiply method with negative numbers. """ math_ops = MathOperations() assert math_ops.multiply(-2, 3) == -6 assert math_ops.multiply(2, -3) == -6 assert math_ops.multiply(-2, -3) == 6 def test_multiply_with_zero(self): """ Test multiply method with zero as one of the inputs. """ math_ops = MathOperations() assert math_ops.multiply(0, 5) == 0 assert math_ops.multiply(5, 0) == 0 assert math_ops.multiply(0, 0) == 0 def test_subtract_with_float_input(self): """ Test subtract method with float input. This tests an edge case for the subtract method. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.subtract(5.5, 3.3) assert round(result, 1) == 2.2 def test_subtract_with_large_numbers(self): """ Test subtract method with very large numbers. This tests scenario 2: input is outside accepted bounds. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.subtract(1e100, 1e99) assert result == 9e99 def test_subtract_with_negative_numbers(self): """ Test subtract method with negative numbers. This tests another edge case for the subtract method. """ math_ops = MathOperations() result = math_ops.subtract(-5, -3) assert result == -2 def test_subtract_with_non_numeric_input(self): """ Test subtract method with non-numeric input. This tests scenario 3: input is incorrect type. """ math_ops = MathOperations() with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.subtract("5", 3) with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.subtract(5, "3") with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.subtract("a", "b") def test_subtract_with_none_input(self): """ Test subtract method with None as input. This tests scenario 1: input is empty and/or invalid. """ math_ops = MathOperations() with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.subtract(None, 5) with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.subtract(5, None) with pytest.raises(TypeError): math_ops.subtract(None, None)
ドキュメント作成機能
プロンプトから/docを実行するだけでREADME.mdが作成されます。
- 作成されたREADME.md
-
# Python Math Operations Library This project provides a simple Python library for basic arithmetic operations. It offers a clean and efficient way to perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and exponentiation. The `MathOperations` class encapsulates these fundamental mathematical functions, making it easy to integrate into various Python projects. Whether you're building a calculator application, working on scientific computations, or need reliable math operations in your codebase, this library offers a straightforward solution. ## Repository Structure The repository has a simple structure with a single Python file: - `test.py`: The main Python file containing the `MathOperations` class. ## Usage Instructions ### Installation No installation is required. Simply copy the `test.py` file into your project directory. ### Getting Started To use the `MathOperations` class in your Python project, follow these steps: 1. Import the class: ```python from test import MathOperations ``` 2. Create an instance of the class: ```python math_ops = MathOperations() ``` 3. Use the methods as needed: ```python result_add = math_ops.add(5, 3) result_subtract = math_ops.subtract(10, 4) result_multiply = math_ops.multiply(6, 7) result_divide = math_ops.divide(15, 3) result_power = math_ops.power(2, 3) print(f"Addition: 5 + 3 = {result_add}") print(f"Subtraction: 10 - 4 = {result_subtract}") print(f"Multiplication: 6 * 7 = {result_multiply}") print(f"Division: 15 / 3 = {result_divide}") print(f"Power: 2^3 = {result_power}") ``` ### Available Methods The `MathOperations` class provides the following methods: - `add(a, b)`: Adds two numbers. - `subtract(a, b)`: Subtracts the second number from the first. - `multiply(a, b)`: Multiplies two numbers. - `divide(a, b)`: Divides the first number by the second. Raises a `ValueError` if attempting to divide by zero. - `power(a, b)`: Raises the first number to the power of the second. ### Error Handling The `divide` method includes error handling for division by zero. If you attempt to divide by zero, a `ValueError` will be raised with the message "Division by zero is not allowed." Example of handling this error: ```python try: result = math_ops.divide(10, 0) except ValueError as e: print(f"Error: {e}") ``` ### Testing & Quality To ensure the reliability of the `MathOperations` class, it's recommended to write unit tests for each method. You can use Python's built-in `unittest` module or a third-party testing framework like `pytest`. ### Troubleshooting 1. **Issue**: Getting unexpected results from mathematical operations. - **Solution**: Double-check the order of operands in subtraction and division operations. Remember that `a - b` subtracts `b` from `a`, and `a / b` divides `a` by `b`. 2. **Issue**: Encountering a `ValueError` when performing division. - **Solution**: This error occurs when attempting to divide by zero. Always check if the divisor is non-zero before performing division: ```python if b != 0: result = math_ops.divide(a, b) else: print("Cannot divide by zero") ``` 3. **Issue**: Results of power operation are unexpectedly large or small. - **Solution**: Be cautious with large exponents as they can lead to very large numbers. For negative exponents, the result will be a float between 0 and 1. ### Performance Optimization The `MathOperations` class uses Python's built-in arithmetic operators, which are generally optimized for performance. However, for large-scale computations or repeated operations, consider: - Using NumPy for array-based operations if dealing with large datasets. - Implementing caching mechanisms for frequently used results. - Profiling your code to identify performance bottlenecks: ```python import cProfile def profile_math_ops(): math_ops = MathOperations() for _ in range(1000000): math_ops.add(5, 3) math_ops.multiply(4, 7) cProfile.run('profile_math_ops()') ``` ## Data Flow The data flow in the `MathOperations` class is straightforward: 1. User creates an instance of `MathOperations`. 2. User calls a method with two numeric arguments. 3. The method performs the specified operation. 4. The result is returned to the user. ``` [User] -> [MathOperations Instance] | v [Method Call (e.g., add(a, b))] | v [Operation Performed] | v [Result Returned to User] ``` Note: All operations are performed in memory without any external data storage or network requests.
コードレビュー機能
こちらも同様にプロンプトから/reviewを実行するだけになります。
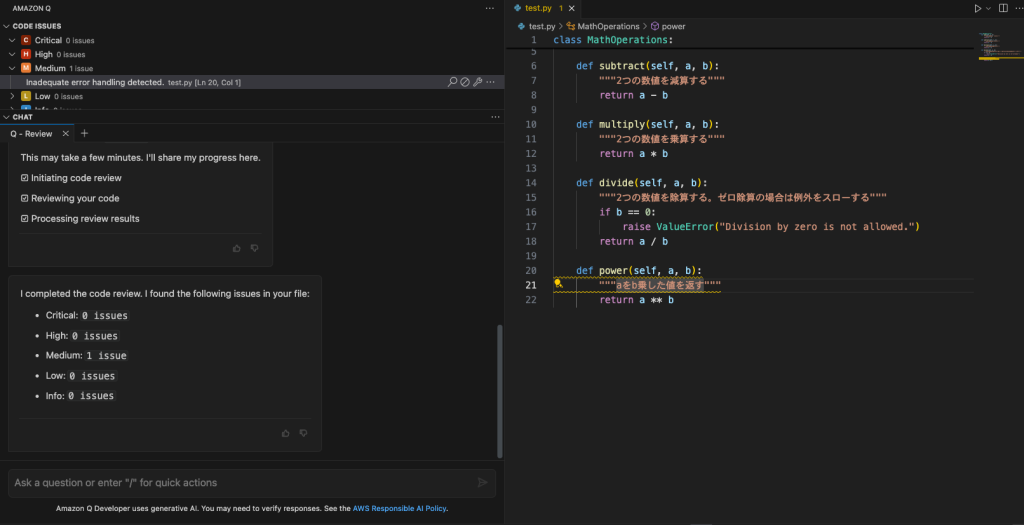
今回は単純なコードでしたので1つしか検出されませんでした。
その他の発表
GitLab Duo with Amazon Qの発表
今回ご紹介したAmazon Q Developerの機能をGitLab上で利用可能となるサービスのプレビューが発表されました。

移行関連の機能
レガシーコードやVMwareからの移行サポート機能が複数発表されました。



運用調査機能
AWS環境の運用調査機能のプレビューが発表されました。CloudWatch 、AWS CloudTrail ログ、デプロイ情報、リソース設定の変更、AWS Health イベントなど、AWS 環境に関するさまざまなシグナルを精査して原因調査をサポートしてくれるようです。

SageMaker関連
SageMaker関連ではAmazon Qとの統合を含めた発表がありました。


さいごに
Amazon Q Developerを利用することでコードの作成だけではなく、修正、運用までをカバーすることが出来る素晴らしいサービスであると感じました。
一方で、ブログ執筆時点では日本語が未対応となるので日本の利用者にとってはそこがハードルとなってしまうのかなと感じました。
今後もさらなるアップデートが予想されるので継続して利用していきたいと思います!
ここまで読んでいただきありがとうございました。